- Identification
- Properties
- Safety Data
- Specifications & Other Information
- Links
- Quick Inquiry
Identification
CAS Number
1772-25-4
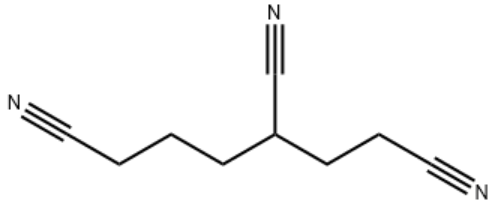
Name
1,3,6-Hexanetricarbonitrile
Synonyms
(±)-1,3,6-HEXANETRICARBONITRILE
1,3,6-Hexanetricarbonitrile [ACD/Index Name] [ACD/IUPAC Name]
1,3,6-Hexanetricarbonitrile [French] [ACD/Index Name] [ACD/IUPAC Name]
1,3,6-Hexantricarbonitril [German] [ACD/IUPAC Name]
1,3,6-TRICYANOHEXANE
1772-25-4 [RN]
217-199-7 [EINECS]
4-Cyanosuberonitrile
UNII :SJY3YNQ3SI
(±)-1,3,6-HEXANETRICARBONITRILE, TECH.
[1772-25-4] [RN]
hexane-1,3,6-tricarbonitrile
MFCD00129792
SMILES
C(CC#N)CC(CCC#N)C#N
StdInChI
InChI=1S/C9H11N3/c10-6-2-1-4-9(8-12)5-3-7-11/h9H,1-5H2
StdInChIKey
LNLFLMCWDHZINJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Molecular Formula
C9H11N3
Molecular Weight
161.204
MDL Number
MFCD00131222
Properties
Appearance
Light yellow to yellow oily liquid
Safety Data
Symbol
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard statements
H334Precautionary Statements
P261 – P284 – P501Supplemental Hazard Statements
Risk of explosion if heated under confinement.
RIDADR
NONH for all modes of transport
WGK Germany
3
MSDS Download
Specifications and Other Information of Our
Identification Methods
HNMR, HPLC
Purity
99.5% min
Water C KF, 50%L07 DMC)
≤100ppm
Shelf Life
1 year
Storage
Store at room temperature away from light
Known Application
1,3,6-Hexanetricarbonitrile is an important electrolyte additive, and the composition of the electrolyte restricts the application of positive and negative electrode materials at high voltages. Traditional organic carbonates, such as linear carbonates like DEC, DMC, EMC, and cyclic carbonates like PC, EC, tend to undergo decomposition at high voltages [2,3]. Therefore, the development of novel organic solvents with a wide electrochemical window, high lithium salt solubility, and low toxicity has become a key focus in the development of high-voltage electrolytes. Nitrile-based organic solvents typically possess a wide electrochemical window, high anodic stability, low viscosity, and high boiling points, among other excellent characteristics [4]. Additionally, the decomposition products of solvents containing nitrile groups are generally carboxylates, aldehydes, or corresponding organic amines, eliminating the generation of toxic CN- ions during usage [5-7]. Nitrile solvents demonstrate a broad electrochemical window and are considered promising new organic solvents. However, in terms of the electrochemical performance of lithium-ion batteries, nitrile solvents still face compatibility issues with the negative electrode. The formation of a mixed system with carbonate solvents or the addition of mixed salts like LiBOB can partially alleviate this issue.
General View of Documents
Links
This product is developed by our R&D company Warshel Chemical Ltd (https://www.warshel.com/).
Quick Inquiry
Fill out our inquiry form and one of our experts will be in touch with you shortly.