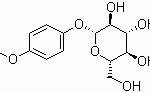
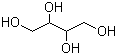
 A recent advancement is carbohydrate pharmaceutics can potentially give way to new generation of carb-based synthetic medication and diagnostic probes. Researchers as Oxford and York Universities have found positive indication that about half of the enzymes which bond sugar and protein molecules together may perform this job by using a rare type of chemical reaction. This finding can lead to creation of new protein-inhibitor based drugs with a broad spectrum uses in clinical therapy.
Carbohydrates have been dubbed as the ‘next frontier’ in biomedicine, but despite their pivotal role in biology, there are surprisingly few carb-based drugs in the market. Carbohydrates have been found useful as diagnostic and therapeutic drugs when it comes to diseases like cancer, Tuberculosis, diabetes, and various heart ailments. Thus, the potency of carbohydrates is not limited to being a source of energy, but it expands further to clinical applications as well.
Let’s see how carbohydrates direct drug development, and how they can be incorporated clinically on a large scale so that the diseases which were complex to treat before can be easily targeted and treated.
A recent advancement is carbohydrate pharmaceutics can potentially give way to new generation of carb-based synthetic medication and diagnostic probes. Researchers as Oxford and York Universities have found positive indication that about half of the enzymes which bond sugar and protein molecules together may perform this job by using a rare type of chemical reaction. This finding can lead to creation of new protein-inhibitor based drugs with a broad spectrum uses in clinical therapy.
Carbohydrates have been dubbed as the ‘next frontier’ in biomedicine, but despite their pivotal role in biology, there are surprisingly few carb-based drugs in the market. Carbohydrates have been found useful as diagnostic and therapeutic drugs when it comes to diseases like cancer, Tuberculosis, diabetes, and various heart ailments. Thus, the potency of carbohydrates is not limited to being a source of energy, but it expands further to clinical applications as well.
Let’s see how carbohydrates direct drug development, and how they can be incorporated clinically on a large scale so that the diseases which were complex to treat before can be easily targeted and treated.More than Sugarcoating: Carbohydrate-based Medicines
 A recent advancement is carbohydrate pharmaceutics can potentially give way to new generation of carb-based synthetic medication and diagnostic probes. Researchers as Oxford and York Universities have found positive indication that about half of the enzymes which bond sugar and protein molecules together may perform this job by using a rare type of chemical reaction. This finding can lead to creation of new protein-inhibitor based drugs with a broad spectrum uses in clinical therapy.
Carbohydrates have been dubbed as the ‘next frontier’ in biomedicine, but despite their pivotal role in biology, there are surprisingly few carb-based drugs in the market. Carbohydrates have been found useful as diagnostic and therapeutic drugs when it comes to diseases like cancer, Tuberculosis, diabetes, and various heart ailments. Thus, the potency of carbohydrates is not limited to being a source of energy, but it expands further to clinical applications as well.
Let’s see how carbohydrates direct drug development, and how they can be incorporated clinically on a large scale so that the diseases which were complex to treat before can be easily targeted and treated.
A recent advancement is carbohydrate pharmaceutics can potentially give way to new generation of carb-based synthetic medication and diagnostic probes. Researchers as Oxford and York Universities have found positive indication that about half of the enzymes which bond sugar and protein molecules together may perform this job by using a rare type of chemical reaction. This finding can lead to creation of new protein-inhibitor based drugs with a broad spectrum uses in clinical therapy.
Carbohydrates have been dubbed as the ‘next frontier’ in biomedicine, but despite their pivotal role in biology, there are surprisingly few carb-based drugs in the market. Carbohydrates have been found useful as diagnostic and therapeutic drugs when it comes to diseases like cancer, Tuberculosis, diabetes, and various heart ailments. Thus, the potency of carbohydrates is not limited to being a source of energy, but it expands further to clinical applications as well.
Let’s see how carbohydrates direct drug development, and how they can be incorporated clinically on a large scale so that the diseases which were complex to treat before can be easily targeted and treated.
© 2025 WATSON INTERNATIONAL LIMITED. All Rights Reserved. This site and all content are protected by international Copyright laws. Third party logos and marks appearing on this website are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective owners and licensors, and all rights therein and thereto are reserved to such entities.

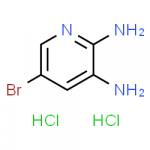
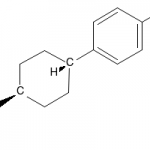
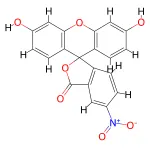
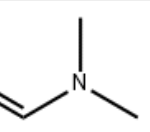
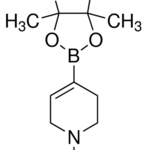
![Structure of 4-[2,6-dioxohexahydropyrimidin-4(S)-ylcarboxamido]-L-phenylalanyl-4-ureido-D-phenylalanyl-L-leucyl-N6-isopropyl-L-lysyl CAS PNA-2731](https://www.watson-int.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Structure-of-4-26-dioxohexahydropyrimidin-4S-ylcarboxamido-L-phenylalanyl-4-ureido-D-phenylalanyl-L-leucyl-N6-isopropyl-L-lysyl-CAS-PNA-2731-150x150.png)